Table of Contents
Introduction
Monero (XMR) is a privacy-focused cryptocurrency that launched on April 18, 2014. It prioritizes user anonymity by obscuring sender, recipient, and transaction amount details on its blockchain. This digital currency utilizes several privacy technologies, including ring signatures, ring confidential transactions, and stealth addresses. These features collectively mask the flow of funds, providing users with a higher degree of privacy than offered by many other cryptocurrencies.

Monero, originally known as BitMonero, was created as a fork of the Bytecoin blockchain. It was developed by seven developers, five of whom chose to remain anonymous. Monero’s main goal is to allow transactions to be private and untraceable, which makes it a preferred option for individuals who value privacy for legitimate reasons. Still, due to its strong privacy features, it also attracts illicit use.
What is Monero (XMR), and how does it work?
Monero (XMR) is a cryptocurrency that emphasizes privacy, launched on April 18, 2014. Unlike many cryptocurrencies, Monero ensures transactions remain confidential and untraceable through its use of ring signatures and stealth addresses. These features obscure the details of both sender and receiver in a transaction, as well as the amount transferred.
The primary technology behind Monero’s privacy features is known as ring signatures. When a transaction is initiated, ring signatures combine the spender’s input with other possible inputs, making it virtually impossible to determine which specific information is being spent. This creates a high level of privacy by concealing the true origin of funds.
In addition to ring signatures, XMR also utilizes stealth addresses. Instead of revealing the recipient’s actual speech, a unique one-time address is generated for each transaction. This means the recipient’s correct address remains hidden from the public, making linking transactions to specific individuals or addresses significantly more challenging.
To further enhance privacy, Monero (XMR) employs confidential transactions. This feature obscures the transaction amounts by using cryptographic proofs. Instead of displaying exact values, the proofs demonstrate that the sums involved in the transaction meet specific criteria without revealing the precise cuts. This ensures that transaction values are kept confidential, adding privacy and fungibility to Monero.
To maintain the network’s security and integrity, Monero relies on a consensus algorithm called Proof-of-Work (PoW). Miners compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain. Monero’s PoW algorithm, CryptoNight, is designed to resist specialized mining hardware, fostering a more equitable mining power distribution.
Monero’s blockchain implements a dynamic block size that adjusts according to transaction volume. This enables scalability and efficient transaction processing, accommodating fluctuations in network activity.
Combining ring signatures, stealth addresses, confidential transactions, and a dynamic block size makes XMR a highly private and secure cryptocurrency. It allows users to conduct transactions without revealing sensitive information, such as the sender’s identity, the recipient’s address, and transaction amounts. This focus on privacy has made Monero a popular choice for individuals who value financial confidentiality and seek to maintain their anonymity in the digital realm.
Why is Privacy Important?
Privacy is important in Monero for several reasons, summarized in the following bullet points:
Financial Confidentiality: XMR ensures that your financial transactions remain private, preventing unauthorized individuals from accessing sensitive information such as your account balance, transaction history, and recipient details.
Protection Against Surveillance: Monero shields users from mass surveillance and monitoring by government agencies, corporations, and other entities that may attempt to track and analyze their financial activities.
Preventing Targeted Attacks: Privacy in XMR prevents potential adversaries from explicitly targeting individuals or groups based on their transaction history, thus reducing the risk of scams, extortion, or other malicious activities.
Preserving Personal Security: By keeping your financial information private, Monero helps protect you from identity theft, fraud, and other financial exploitation if your data falls into the wrong hands.
Business Confidentiality: Privacy features in Monero are crucial for businesses, as they safeguard their transaction records, financial dealings, and trade secrets from competitors, suppliers, and other third parties.
Fostering Financial Inclusion: Monero’s privacy preserves individuals’ dignity by allowing them to conduct financial transactions without fear of discrimination or exclusion based on their economic history.
Enhanced Fungibility: Privacy in XMR ensures that each cryptocurrency unit is interchangeable with any other, regardless of its transaction history. This leads to increased fungibility and makes it harder to trace individual coins’ origins.
Protecting Personal Relationships: Monero’s privacy prevents the exposure of sensitive financial transactions, safeguards personal relationships, and prevents potential conflicts or unnecessary intrusions into one’s personal life.
Avoiding Price Manipulation: With privacy, Monero users are shielded from malicious actors attempting to manipulate the market by analyzing their transaction patterns and using that information to their advantage.
Upholding Civil Liberties: Privacy is a fundamental right that XMR helps keep, allowing individuals to exercise their freedom of financial expression and maintain control over their financial information.
It’s worth noting that while privacy is a crucial feature of Monero, it also presents particular challenges in terms of regulatory compliance and criminal investigations, as it can potentially be misused by individuals engaging in illegal activities.
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Monero (XMR)
Monero, a digital cryptocurrency known for its high privacy and decentralization features, has been a topic of interest in financial tech. Like any other technology, XMR has its advantages and disadvantages. Let’s delve deeper into understanding each one.
Advantages of Monero
1. Privacy
Privacy is arguably the most significant advantage of Monero (XMR). In the age of digital transactions, privacy has become a critical concern. Monero considers this by providing a platform where transactions cannot be tracked. This is possible by Monero’s using ring signatures and stealth addresses, which conceal the details rather than transactions. Ring signatures obscure the sender’s identity by mixing their trade with others, making establishing a link between each subsequent transaction difficult.
Similarly, stealth addresses provide additional security by creating random one-time addresses for every transaction on behalf of the recipient. This means that your transactions remain confidential, and your identity remains anonymous unless you disclose it.
2. Fungibility:
Another critical advantage of XMR is its fungibility, which means every currency unit can be interchanged with another without any difference. This characteristic is crucial because it ensures no coins are tainted or associated with nefarious activities. In contrast, with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, exchanges can track and block coins associated with illegal operations, potentially limiting their usability. Monero’s inherent privacy features ensure that each coin’s history is untraceable, thus preserving its fungibility.
3. Decentralization
Unlike many other cryptocurrencies, XMR promotes true decentralization. It uses a proof-of-work algorithm resistant to ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit), miners, thereby preventing mining centralization. This equality-driven approach allows anyone with a computer to contribute to network security, maintaining the democratic ethos at the heart of cryptocurrency philosophy.
4. Dynamic Scalability:
Monero has no fixed block size limit. Instead, it uses a dynamic block size that changes based on the demand of the network. This makes it more adaptable to increases in transaction volume.
Disadvantages of Monero
1. Scalability Issues
Despite its dynamic scalability, XMR has been criticized for its scalability issues. Monero’s commitment to privacy and security leads to significantly larger transaction sizes than other cryptocurrencies. These more significant transactions require more storage space and can lead to slower confirmation times and higher transaction fees, particularly during periods of high activity.
2. Legal Concerns
While privacy is a significant advantage of XMR, it also presents a major disadvantage. The high level of privacy has made Monero a favored cryptocurrency for illicit activities on the internet. This has attracted the attention of regulatory bodies worldwide, leading to potential legal ramifications for users. Some exchanges have delisted XMR due to these concerns, which could impact its liquidity and utility.
3. Complexity and User Experience
Monero’s advanced privacy features add a layer of complexity that may not appeal to the average user. Although these features are beneficial, they can confuse and intimidate newcomers, potentially hindering widespread adoption. For instance, the process of creating and managing multiple one-time addresses could be seen as cumbersome to some users.
4. Market Acceptance:
Despite its technological advantages, XMR is not as widely accepted or recognized as other cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum. This could limit its potential for growth and mainstream adoption.
While Monero (XMR) offers robust privacy features, fungibility, and fair mining practices, it also faces significant challenges, including scalability issues, potential legal concerns, and a steep learning curve for new users. As with any investment, potential users should conduct thorough research and understand the benefits and risks associated with Monero before getting involved.
Monero features
Monero (XMR), a decentralized cryptocurrency, offers several distinctive features that set it apart from other digital currencies. These features primarily focus on privacy, security, and fungibility, making XMR a popular choice for individuals who prioritize financial confidentiality and anonymity.

Ring Signatures
It utilizes ring signatures, a cryptographic technique that combines the spender’s transaction input with other possible information. This creates uncertainty, making determining the true origin of funds challenging. With ring signatures, linking a specific sender to a transaction becomes nearly impossible, enhancing privacy.
Stealth Addresses
Monero (XMR) employs stealth addresses, which provide an additional layer of privacy for recipients. When a user provides a stealth address, a unique one-time address is generated for each transaction. This address is derived from the recipient’s public key but does not directly reveal their identity. By using stealth addresses, the actual address of the recipient remains hidden, making it difficult to trace transactions.
Confidential Transactions
Monero incorporates confidential transactions to obfuscate transaction amounts. Instead of revealing exact values, confidential transactions use cryptographic proofs to demonstrate that the sums being sent satisfy certain conditions without revealing the actual charges. This feature prevents outsiders from quickly discerning the precise amounts involved in XMR transactions, preserving privacy and fungibility.
Adaptive Block Size
Monero’s blockchain implements a dynamic block size that adjusts according to transaction volume. This scalability feature allows for the efficient processing of transactions, accommodating fluctuations in network activity while ensuring quick confirmation times and low transaction fees.
Fungibility
Monero strongly emphasizes fungibility, the property that all currency units are interchangeable and indistinguishable. Due to its privacy features, XMR ensures that each unit of its currency is equal in value and cannot be tainted or discriminated against based on its transaction history. This fungibility promotes acceptance and usability as each coin is equally desirable and reliable.
Mining Algorithm
XMR employs a mining algorithm called CryptoNight, which is designed to resist specialized mining hardware. This approach aims to ensure a more egalitarian distribution of mining power and prevent network centralization. The algorithm also promotes energy efficiency by allowing for CPU mining.
These features collectively create a privacy-focused cryptocurrency that offers users enhanced anonymity and confidentiality in their financial transactions. Monero’s commitment to privacy and fungibility makes it an attractive choice for individuals who value their economic sovereignty and seek to maintain their anonymity in the digital world.
Monero vs. Bitcoin: A Privacy Comparison
The table below shows a privacy comparison features of Monero and Bitcoin:
| Privacy Feature | Monero | Bitcoin |
| Transaction Privacy | Provides strong privacy by using ring signatures, stealth addresses, and RingCT to obfuscate sender, recipient, and transaction amounts. | Offers pseudonymity as transactions are recorded on a public ledger (blockchain), but identities can potentially be linked to addresses through analysis and tracking. |
| Transaction Linkability | Difficult to link transactions due to ring signatures and stealth addresses, making it challenging to trace the flow of funds. | Transaction graph analysis can reveal transaction histories, allowing for potential linkage between addresses and the flow of funds. |
| Address Privacy | Transaction amounts are visible on the blockchain, enabling anyone to see the transferred value. | Addresses are transparent and publicly visible on the blockchain, allowing anyone to view transaction details and associated balances. |
| Amount Privacy | RingCT protocol conceals transaction amounts, ensuring the privacy of the transferred value. | Monero’s privacy features enhance fungibility by making each currency unit indistinguishable, ensuring that all coins have equal value. |
| Fungibility | XMR privacy features enhance fungibility by making each currency unit indistinguishable, ensuring that all coins have equal value. | Due to the transparent nature of Bitcoin, certain coins may be blacklisted or considered less valuable due to their transaction history, potentially affecting fungibility. |
| Network Analysis | Monero’s privacy features make network analysis and transaction tracing significantly more challenging. | Bitcoin’s transparent blockchain enables network analysis, allowing observers to analyze transaction patterns and potentially trace transactions. |
| Privacy Default | Privacy is the default in XMR, ensuring that all transactions are private unless users specifically choose to disclose information. | Bitcoin transactions are public by default, and additional steps are required to enhance privacy (e.g., using mixers or privacy-enhancing wallets). |
How Monero (XMR) Differs from Bitcoin (BTC)
Monero and Bitcoin, both stemming from a decentralized ideology, exhibit significant differences primarily in their approach to privacy, mining, and transaction policies.

Monero (XMR) is renowned for its stringent privacy features, which are inherent and automatic in every transaction. It uses technologies such as ring signatures, stealth addresses, and Ring Confidential Transactions (RCTs) to ensure that transactions are confidential and untraceable by anyone other than the transaction participants themselves. This contrasts sharply with Bitcoin, which maintains a transparent ledger where transactions are pseudonymous but can be traced if a wallet address is ever linked to an individual.
The mining mechanisms between the two also differ greatly. Monero uses a Proof-of-Work (PoW) algorithm called RandomX, which is designed to be ASIC-resistant, allowing it to be mined effectively using ordinary computers. This promotes greater decentralization as it discourages the development of mining pools that dominate the network, a situation more common in Bitcoin’s network, which relies on ASICs for mining. Bitcoin’s SHA-256 mining algorithm benefits significantly from this specialized hardware, leading to a more centralized mining landscape.
In terms of transaction policies, Monero provides more flexibility than Bitcoin. Monero’s block size is dynamic, which helps it adapt to network demand without raising transaction fees. Bitcoin, on the other hand, has a fixed block size, which can lead to increased transaction fees during periods of high demand.
Overall, while Bitcoin holds the upper hand in terms of recognition and widespread use, Monero appeals to those prioritizing privacy and seeking to avoid the centralization of network power in the hands of few large-scale miners.
How to Buy and Store Monero (XMR)
To buy and store Monero (XMR) securely, follow these comprehensive steps:
Step 1: Choose a Cryptocurrency Exchange
Select a reliable cryptocurrency exchange that supports Monero. Popular choices include Kraken and Binance due to their security features, user-friendly interfaces, and support for various payment methods. Ensure the exchange is reputable by checking its security measures, customer service, and regulatory compliance.
Step 2: Set Up and Verify Your Account
Create an account on the chosen exchange. This process typically involves providing an email address and some form of identity verification as part of the exchange’s Know Your Customer (KYC) policy. This step is crucial for security and regulatory compliance.
Step 3: Deposit Funds
Fund your exchange account using a suitable payment method. Most exchanges support funding through bank transfers, credit cards, or other cryptocurrencies. Each method has different transaction speeds and fees, with bank transfers generally being cheaper but slower than credit card transactions.
Step 4: Purchase Monero
Once your account is funded, you can purchase Monero (XMR). You can do this through a direct market order, where you buy at the current market price, or a limit order, where you set a specific price at which you want to buy XMR.
Step 5: Transfer Monero to a Secure Wallet
For enhanced security, transfer your Monero (XMR) from the exchange to a hardware wallet like Ledger Nano X or Ledger Nano S. Hardware wallets store your private keys offline, providing an extra layer of security against hacks. Remember to keep any recovery phrases or private keys in a secure location.
Storing Monero
When it comes to storing Monero, using a hardware wallet is recommended due to its robust security measures. If you prefer a more accessible option, software wallets on your mobile device or computer can also be used, but they are generally less secure than hardware wallets.
By following these steps, you can securely purchase and store Monero (XMR), ensuring the safety of your funds and compliance with regulatory requirements. To protect your investments, always stay updated with the latest security practices and exchange policies.
The Future of Monero (XMR)
Monero (XMR), known for its privacy-centric features, shows a varied outlook in price predictions from various analysts for the coming years.
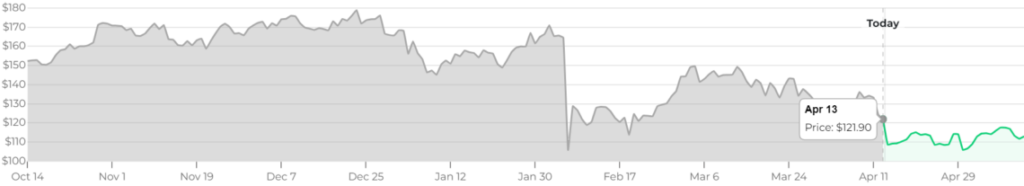
For the year 2024, price forecasts indicate a moderate fluctuation with a potential high around $205.41 and a low near $133.80. Moving into 2025, the predictions suggest a slight rise with an average price potentially around $233.90 and a maximum reaching up to $268.53. Analysts forecast a further increase by 2026, with average prices anticipated around $363.70 and a peak that could edge close to $391.21.
The long-term outlook for Monero (XMR) remains positive, with some ambitious projections for 2030 suggesting that the price could range between $1704 and $2049. These predictions reflect general optimism about the adoption of privacy-focused cryptocurrencies and their relevance in the market.
While the price of Monero (XMR) is subject to the typical volatility of cryptocurrency markets, influenced by regulatory developments, technological advancements, and market sentiment, the overarching trend captured by analysts points to a gradual increase in value over the decade. Given the speculative nature of the crypto market, investors need to consider these projections cautiously.
Recent Developments
Recent updates to this cryptocurrency highlight its robust focus on privacy and security, continuing its role as a key player among privacy-oriented digital currencies. The latest version of its GUI software, tagged ‘Fluorine Fermi’, was released, incorporating important enhancements such as the correction of automatic fee selection and expanded hardware wallet support.
Community-driven initiatives remain strong, with multiple crowdfunding proposals aimed at furthering development and enhancing security measures. These initiatives include significant projects to upgrade various wallet functionalities and integrate new cryptographic proofs to strengthen privacy.
Development activity has also been fervent, with numerous contributions over recent weeks addressing everything from core system updates to peripheral enhancements that aid in maintaining operational excellence and user trust.
Community and developer engagement continues to thrive, with platforms like Monero Talk driving discussions on future research directions and technological advancements, emphasizing the need for ongoing innovation in transaction speed and cryptographic security.
Market Performance Speculations
Monero (XMR) currently holds the 49th position in cryptocurrency market rankings, with a price of $115.88. Monero, known for its strong privacy features, often experiences market fluctuations similar to other digital currencies. This privacy-centric crypto has seen various market dynamics in the past, typically influenced by broader market trends and regulatory news.
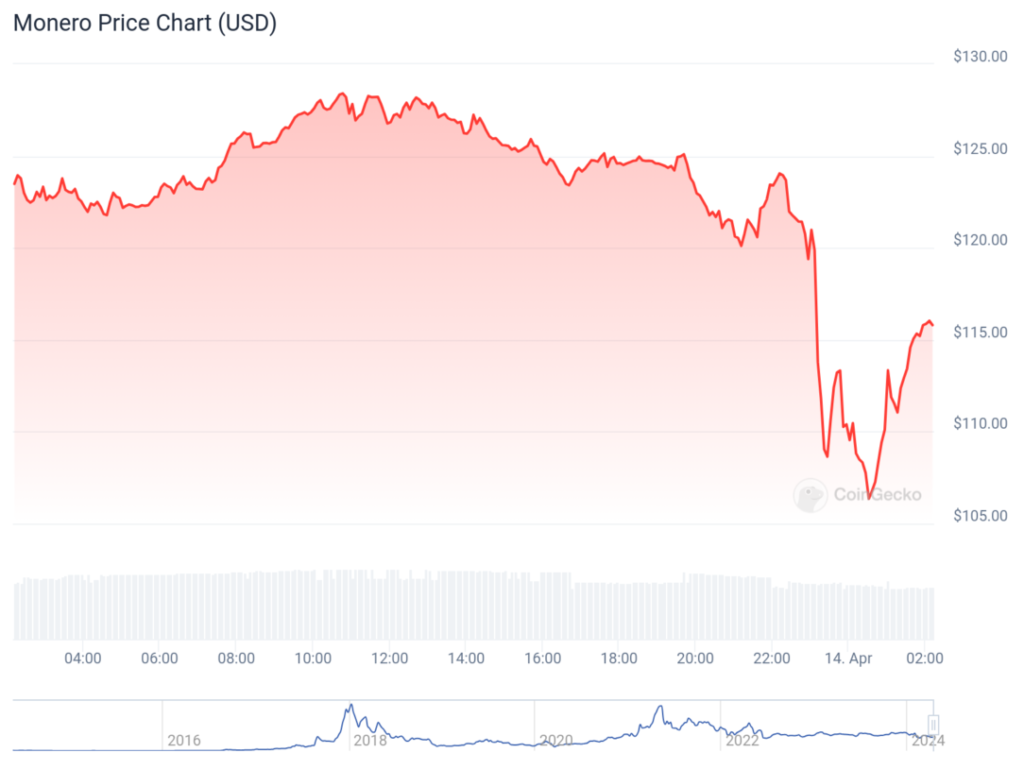
Historically, Monero’s value has responded to changes in market sentiment regarding privacy coins, technological upgrades, and shifts in regulatory landscapes. For instance, past surges in Monero’s price have coincided with increased concerns over online privacy. Conversely, regulatory crackdowns on privacy-focused cryptocurrencies have led to price dips.
Understanding Monero’s market performance requires analyzing these external factors alongside its technological advancements and community support. The future market movements of crypto will likely continue to be shaped by these elements, although exact future trends remain uncertain without speculative assertions.
In conclusion, Monero (XMR) stands out in the cryptocurrency market for its strong commitment to privacy and security. Its use of technologies like ring signatures, stealth addresses, and confidential transactions ensures that user transactions remain anonymous and untraceable. However, these features also introduce scalability challenges and regulatory scrutiny.
FAQs
What is Monero (XMR)?
It is a privacy-focused cryptocurrency that prioritizes anonymous transactions and financial privacy.
How does it ensure privacy?
XMR employs ring signatures, stealth addresses, and confidential transactions to obfuscate transaction details and protect user identities.
Is it completely anonymous?
While XMR provides strong privacy features, it is important to note that no system can guarantee absolute anonymity. However, it significantly enhances privacy compared to other cryptocurrencies.
How is Monero (XMR) different from Bitcoin?
Unlike Bitcoin, XMR offers enhanced privacy through features like ring signatures and confidential transactions, making it much harder to trace transactions and link them to specific individuals.
Can it be traced?
XMR privacy features make tracing transactions or identifying the parties involved extremely difficult. Its decentralized nature and privacy-focused design provide a high level of anonymity.
Can it be used for illegal activities?
Like any other financial tool, Monero can be used legally and illegally. However, its privacy features do not inherently promote or encourage illegal activities; rather, they are designed to protect individual privacy rights.
Is it widely accepted?
While Monero’s adoption is growing, it may not be as widely accepted as more mainstream cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. However, an increasing number of businesses and platforms accept Monero as a form of payment.
Can Monero (XMR) be mined?
Yes, XMR can be mined using CPUs and GPUs. However, it is worth noting that Monero has implemented measures to discourage mining centralization and ensure a fair distribution of rewards.


Add a Comment